1. Can your sonochemistry horn be used in an acid (alkali) environment?
Under the acid (alkali) environment, the horn need to be customized according to the actual working conditions of customers.
2. Can the ultrasonic sonochemistry work continuously?
Yes , it can work 24hours continue.
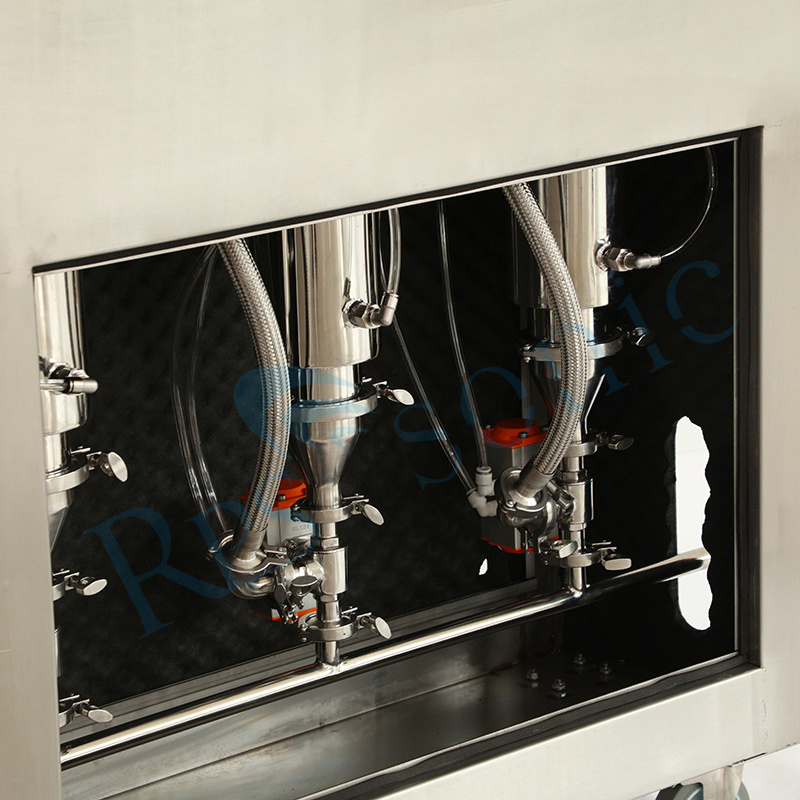
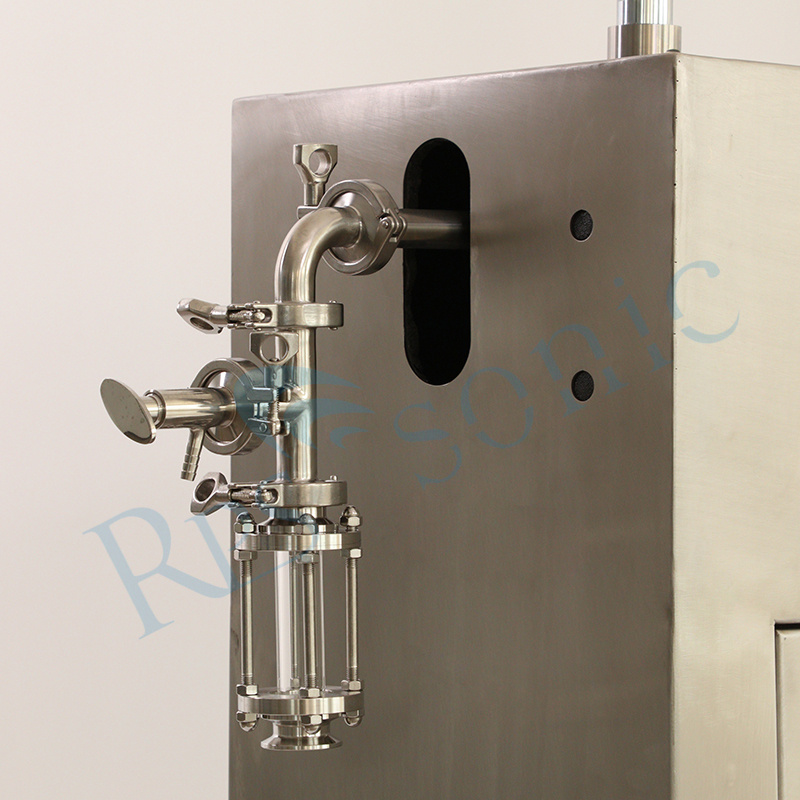
3. What kind of material is the horn?
Titanium alloy, we also customized ceramic horn for customer before.
4. What’s the time of delivery
For Conventional horn, 3 days, for customized horn 7 work days.
5. Does ultrasonic extraction also require the addition of a chemical catalyst?
No , but some time need Mechanical stirring.
6. What’s the advantage of ultrasonic extraction?
Decline the extraction time, and increase the extraction ratio.
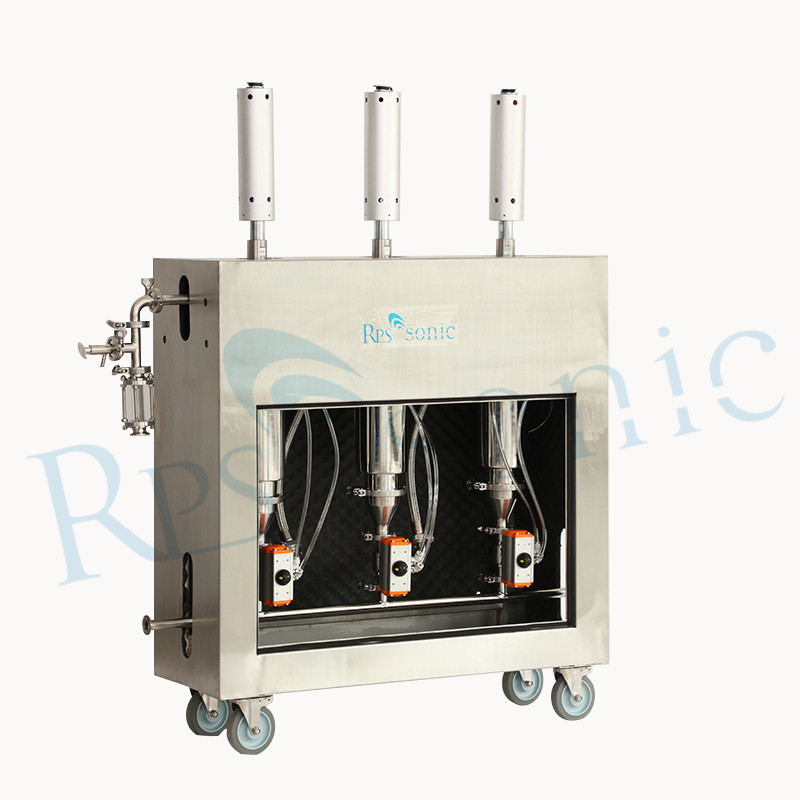
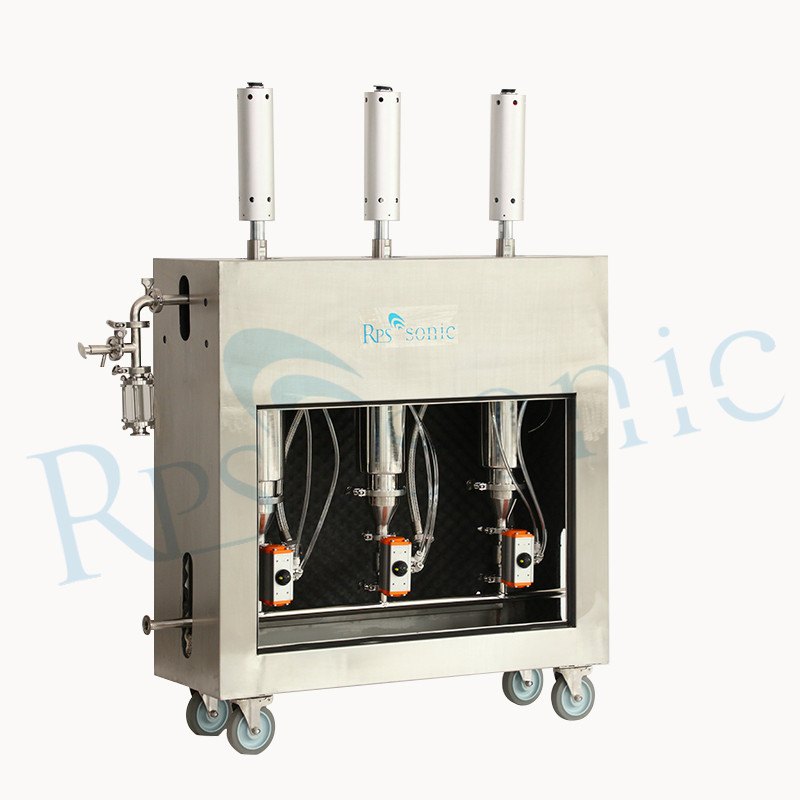
7. What’s the Processing capacity of one set ultrasonic extraction equipment?
Different horn different Processing capacity, for 2000W Nine-section whip horn can dealing 2L~10L/min.
8. Are you manufacturer?
We only manufacturer the transducer and generator our-self, for the horn , we design and buy raw material ,and process by other companies.
9. What’s the warranty of your sonochemistry equipment?
All equipment one year warranty.
10. Do you have Foreign agent?
No, our price already very low for everyone, no agent. We have OEM customer in USA and Germany.
11. Is it difficult to install the ultrasonic sonochemistry equipment?
No , it is easy , we will share Installation diagram, also can take install video for you.