Applications of Ultrasonic Degassing Equipment in the Medical Field
In the medical field, the purity, stability, and cleanliness of liquids directly affect drug efficacy, diagnostic accuracy, and patient safety. Tiny air bubbles in injection solutions can cause air embolism, dissolved oxygen in medications can lead to the oxidation and inactivation of bioactive components, air bubbles in test samples can distort experimental data, and gases in surgical instrument cleaning solutions can weaken disinfection and cleanliness. Traditional degassing methods either rely on high temperature and pressure or require the addition of chemical reagents, making them unsuitable for the stringent requirements of the medical field for gentleness, pollution-free processes, and high precision. Ultrasonic degassing equipment, leveraging the physical properties of acoustic cavitation, offers advantages such as normal temperature and pressure, no chemical additives, and high efficiency and thoroughness. It has become a core supporting device in medical preparations, clinical diagnosis and treatment, and laboratory testing, empowering the safety and accuracy of the medical industry.
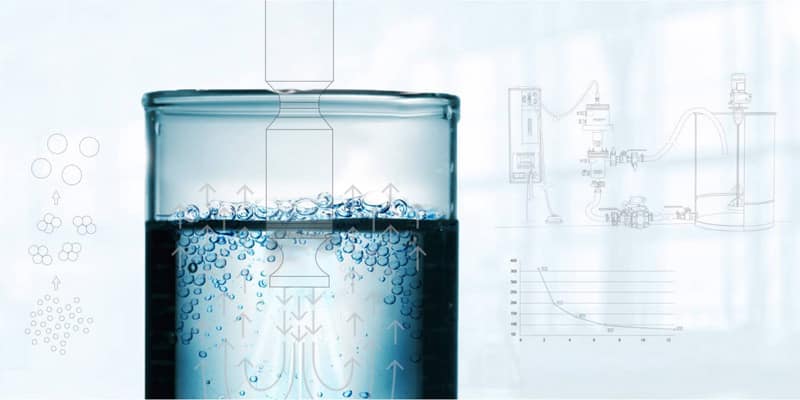
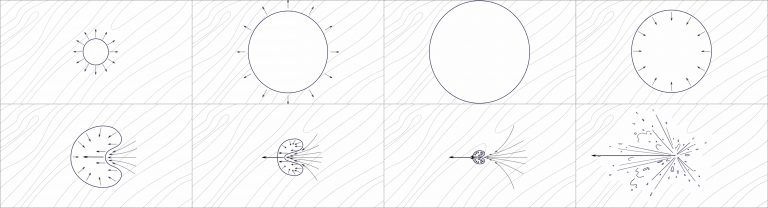
I. Core Principle: The core working principle of ultrasonic degassing equipment is to utilize high-frequency ultrasound to excite the cavitation effect in the liquid, achieving the complete removal of dissolved gases and tiny air bubbles through physical means. The entire process does not alter the liquid composition or damage active substances, perfectly meeting the processing needs of heat-sensitive, easily oxidized, and highly reactive liquids in the medical field. The core process consists of three stages:
First, the ultrasonic generator converts the power frequency current into a high-frequency electrical signal of 20–40kHz, which is then converted into mechanical vibration of the same frequency by a transducer and transmitted into the liquid. The vibration waves create alternating positive and negative sound pressures. During the negative pressure phase, the intermolecular forces in the liquid are broken, generating micron-sized vacuum cavitation bubbles. Subsequently, during expansion, the cavitation bubbles directionally adsorb dissolved oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases from the liquid, rapidly growing and merging into tiny bubbles. Finally, the bubbles rise to the liquid surface and burst, releasing the gas, or collapse under positive pressure, expelling the gas and achieving complete separation of the liquid and gas. The entire process generates only a negligible amount of heat, avoiding component degradation caused by high temperatures, and requires no chemical reagents, eliminating secondary pollution at the source.
Second, core applications in the medical field: Due to its precise, gentle, and clean characteristics, ultrasonic degassing equipment has deeply penetrated key scenarios such as medical preparations, clinical diagnosis and treatment, laboratory testing, and instrument cleaning, becoming a crucial link in ensuring medical quality. Its application value far exceeds that of ordinary degassing equipment.
1. Pharmaceutical Formulation Manufacturing: In the production of injections, biologics, vaccines, and medical gels, degassing is a crucial process determining drug quality and shelf life. Ultrasonic degassing equipment can be precisely tailored to the characteristics of different formulations, achieving efficient degassing while protecting bioactive components. For shear-sensitive biologics such as mRNA vaccines and antibody drugs, high-frequency ultrasound (27kHz) can precisely burst bubble nuclei smaller than 50nm. Combined with a low-temperature control system, this can increase the encapsulation rate of lipid nanoparticles to 99.5% while avoiding damage to protein molecular structures. For ordinary injections, according to USP pharmacopoeia standards, ultrasonic degassing with 80–120W power for 30 seconds can effectively control particle content, ensuring that no more than 25 particles ≥10μm are present in a 25ml sample, meeting the safety standards for injections. Data from a pharmaceutical company shows that vaccine stock solutions treated with ultrasonic degassing exhibited a jump in homogeneity from 89% to 98.7%, a reduction in oxidative degradation rate of over 60%, and a significant extension of product shelf life.
2. Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment Assistance: In clinical infusion and interventional procedures, air bubbles in liquids can pose serious safety hazards. Ultrasonic degassing equipment provides crucial protection for treatment safety. Short-term ultrasonic degassing of the medication solution before intravenous infusion can thoroughly remove free air bubbles and dissolved gases, preventing air embolism caused by air bubbles entering the bloodstream. This requirement complements ultrasonic air embolism monitoring equipment; the former reduces air bubbles at the source, while the latter detects them in real time, thus doubly strengthening the safety defense line for treatment. Furthermore, in the preparation of novel medical consumables such as biodegradable microneedles and medical dressings, ultrasonic degassing can remove microbubbles from the material solution, ensuring the complete formation of microneedle tips and the uniform texture of dressings, avoiding problems such as uneven drug delivery and poor adhesion caused by air bubbles.
3. Laboratory Detection and Sample Processing: In medical laboratories, experiments such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), particulate detection, and pathogen detection have extremely high requirements for sample purity. The presence of air bubbles can lead to baseline drift, ghost peaks, and data distortion. Ultrasonic degassing equipment, as a standard auxiliary device in laboratories, can quickly process test samples and mobile phases. For example, ultrasonic degassing of sterile powder solutions for 30 seconds can effectively eliminate bubble interference, ensuring accurate and reliable test results. In scenarios such as infectious disease detection and liquid biopsy, ultrasonic degassing can be combined with a disruption function to remove sample bubbles while simultaneously disrupting cells and releasing target substances (such as viral nucleic acids and tumor markers), improving detection sensitivity and efficiency. The multi-functional ultrasonic equipment purchased by institutions such as the Jilin University Sino-Japanese Friendship Hospital has become a crucial step in sample pretreatment, providing support for accurate diagnosis.
III. Core Advantages of Medical-Grade Equipment: Compared to traditional degassing methods, the adaptability of ultrasonic degassing equipment in the medical field stems from its unique advantages, perfectly meeting the core requirements of the medical industry for safety, accuracy, and compliance:
• Gentle and non-damaging, protecting active ingredients: Operating at room temperature and pressure, without the degradation of components caused by high temperature and pressure, and without mechanical shearing damage to the structure of biological agents, it can adapt to the processing needs of all categories, from ordinary pharmaceutical solutions to high-end biological agents.
• Physically additive-free, meeting cleanliness standards: No defoamers, degassing agents, or other chemical reagents are required throughout the process, avoiding secondary contamination and meeting GMP production standards and medical-grade hygiene requirements. It is particularly suitable for sterile, residue-free diagnostic and treatment scenarios.
• Precise and controllable, adaptable to diverse needs: Frequency, power, and processing time can be precisely adjusted. For example, 80–120W is suitable for degassing test samples, while a high-power pulse mode is suitable for high-viscosity formulations. Combined with temperature monitoring, it ensures a stable and controllable processing flow.
• Highly efficient, convenient, and highly integrated: Degassing efficiency is 30%-70% higher than traditional static or heating methods. It can be quickly integrated into formulation production lines, laboratory processes, and cleaning equipment to achieve batch processing and continuous online operation.
IV. Application Standards and Maintenance Points in the Medical Field The unique characteristics of the medical field place higher demands on the operation and maintenance of ultrasonic degassing equipment, requiring strict adherence to compliance standards and operating procedures:
1. Parameter Compliance and Adaptation: Parameters must be set strictly according to pharmacopoeia standards and formulation characteristics. For example, degassing of injectable drugs requires controlling the power at 80–120W and the time at 30 seconds to 2 minutes to avoid inappropriate parameters affecting drug quality or test results. After processing different types of liquids, the equipment cavity must be cleaned to prevent cross-contamination.
2. Compliant Equipment Selection: Select equipment that meets medical-grade standards. Components in contact with liquids must be made of corrosion-resistant and easily disinfectable materials such as stainless steel or titanium alloys. The equipment should have automatic frequency tracking and fault alarm functions to ensure safe and stable operation.
3. Regular Calibration and Maintenance: Regularly calibrate the ultrasonic power, frequency, and temperature monitoring functions. Clean the transducer and vibrating carrier to remove residual liquid and dirt to prevent obstruction of vibration transmission. After long-term use, check the wiring connections to ensure the equipment meets clinical safety requirements.
4. Efficacy Verification Testing: The degassing effect is verified by measuring the dissolved oxygen content in the liquid (medical-grade target value <1mg/L), or by combining methods such as particulate matter detection and chromatographic analysis, ensuring compliance with diagnostic and production standards.
V. Future Development Trends: With the iteration of medical technology, ultrasonic degassing equipment is upgrading towards intelligence and customization to further adapt to the high-end needs of the medical field. On the one hand, intelligent closed-loop control systems will become mainstream, using integrated sensors to monitor the liquid's gas content, viscosity, and temperature in real time, automatically adjusting ultrasonic parameters to achieve precise control of the degassing process. On the other hand, scenario-specific customized models are constantly emerging, such as low-temperature degassing models for biological agents, miniaturized precision models for laboratories, and integrated degassing modules for cleaning equipment.
Simultaneously, the synergistic application of ultrasonic degassing technology with vacuum and cryogenic technologies will become increasingly widespread, further improving degassing efficiency and component protection through combined processes, adapting to the needs of emerging medical technologies such as mRNA vaccines and cell therapy. As a core device for liquid purification in the medical field, ultrasonic degassing equipment is strengthening the safety defense line for diagnosis and treatment through technological innovation, providing important support for the high-quality development of the medical industry.

 English
English














