Vacuum glass, hailed as the "king of transparent thermal insulation materials," has become a key material in building energy conservation, high-end home appliances, and precision instruments due to its superior thermal insulation, sound insulation, and anti-condensation properties. However, its core "vacuum" and "sealing" characteristics place almost stringent demands on manufacturing processes, especially the reliability of edge metal sealing. Traditional hot-melt or flame welding methods often suffer from oxidation, incomplete soldering, and thermal stress concentration, becoming the "Achilles' heel" limiting the performance and lifespan of vacuum glass. Now, a technology originating from precision electronics manufacturing—ultrasonic soldering iron tin plating—is quietly breaking through this bottleneck, bringing a silent but profound technological revolution to the vacuum glass industry.
I. Traditional Challenges: Analysis of the "Pain Points" in Vacuum Glass Sealing The typical structure of vacuum glass involves constructing a vacuum cavity of less than 0.3 mm between two panes of glass, with a permanent hermetically sealed connection achieved by a fused metal alloy (such as lead-tin alloy or copper alloy). The ultimate goal of this process is to achieve "zero leakage, high strength, and low heat loss." Traditional soldering processes face three core challenges:
Oxidation Obstacles: During high-temperature soldering, an oxide layer easily forms on the metal surface, hindering solder flow and wetting, leading to discontinuous welds and micropores, creating a potential for chronic leaks later.
Heat Damage Risk: Glass is extremely sensitive to localized thermal shock. The significant thermal stress generated by traditional high-temperature soldering can cause microcracks or structural deformation in the glass, affecting its strength and optical properties.
Difficulty in Precision Control: Welds are typically as narrow as millimeters, requiring precise solder spreading. Traditional methods struggle to find a perfect balance between avoiding oxidation and precise heat control.
II. Technical Principles: How Does Ultrasonic Soldering "Activate" the Soldering Process?
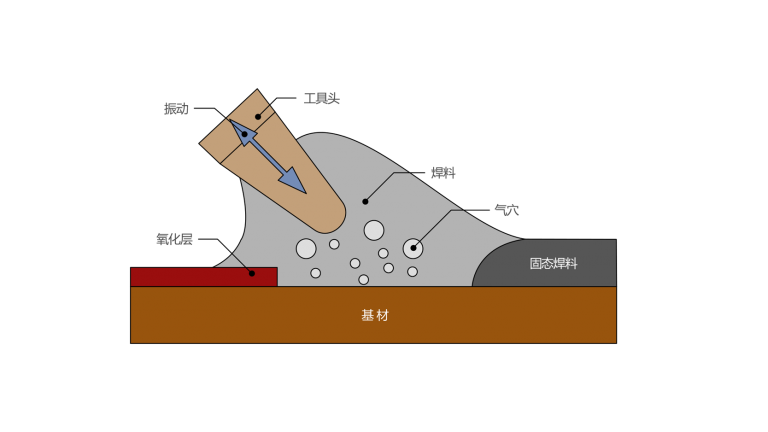
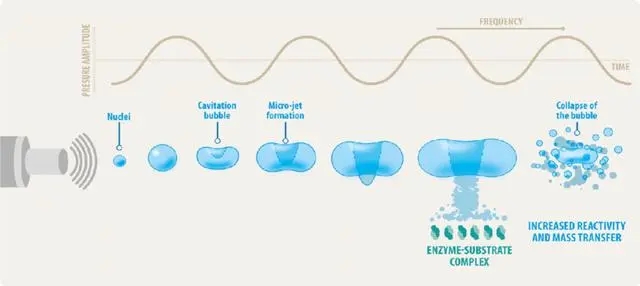
Ultrasonic soldering iron tin plating technology cleverly combines high-frequency mechanical vibration (typically 20kHz-60kHz) with a precisely temperature-controlled soldering iron tip. Its core principle lies in the cavitation and mechanical friction effects of ultrasound:
Cavitation Cleaning: Ultrasonic waves generate countless tiny vacuum bubbles in the molten solder, which collapse instantly. The resulting powerful shock waves completely peel away the oxide film and contaminants from the surface of the workpiece (such as a metal sealing ring on glass), exposing an absolutely clean, active metal surface.
Friction Wetting: High-frequency vibrations generate microscopic friction and agitation at the solid-liquid interface, significantly reducing the surface tension and interfacial energy of the molten solder. This allows it to spread rapidly and uniformly at lower temperatures and penetrate into the micropores of the substrate, forming a dense metallurgical bond.
Low-Temperature Advantage: Because ultrasound significantly improves the fluidity and wettability of the solder, welding can be completed at temperatures 30-100°C lower than traditional methods, greatly reducing heat input.
III. Application Empowerment: Specific Practices of Ultrasonic Tin Plating in Vacuum Glass Manufacturing
On the vacuum glass production line, this technology primarily empowers two key stages:
**Pre-tin Plating Treatment of Metal Sealing Rings:** Before the glass and sealing ring are officially sealed, the sealing ring (e.g., Kovar alloy, stainless steel rings) is pre-tin-plated using an ultrasonic soldering iron. Ultrasonic waves ensure that the solder (e.g., high-purity tin-based alloy) forms an ultra-thin, uniform, and oxidation-free active coating on the ring surface. This "perfect" pre-coating layer lays a reliable foundation for subsequent sealing with the corresponding metal layer on the glass, increasing the final seal strength by over 30% and significantly reducing seal porosity.
**Precision Repair and Reinforcement of Sealing Welds:** For completed vacuum glass edge sealing, or for localized areas of poor wetting discovered during manufacturing, traditional methods are insufficient for repair. Ultrasonic welding torches equipped with ultra-fine soldering tips can perform "minimally invasive surgery," precisely repairing or reinforcing specific points under extremely low heat impact, effectively improving product yield and long-term reliability.
IV. Transformative Advantages: Why is it a "boon" for the vacuum glass industry?
Ultimate Reliable Sealing: Eliminates oxidation-induced weld defects at the source, resulting in dense, continuous welds with excellent gas barrier properties, ensuring a vacuum lifespan (up to 20 years or more).
Guardian of Glass Safety: Low-temperature welding significantly reduces thermal stress, protecting the strength and flatness of the glass body and lowering the risk of spontaneous breakage.
Improved Efficiency and Consistency: The welding process is fast (typically completed in seconds), parameters are easily digitally controlled, suitable for automated integration, improving production cycle time and product consistency.
A Driver of Green Manufacturing: In most cases, corrosive fluxes are unnecessary, reducing cleaning steps and chemical pollution, making it more environmentally friendly and healthier.
Optimized Cost-Effectiveness: Although there is an initial investment in equipment, by improving yield (according to industry cases, it can reduce scrap rate by 5%-15%), reducing rework, and extending product lifespan, the total life cycle cost is significantly optimized.
V. Prospects and Outlook: Towards a Broader Future
Currently, ultrasonic soldering iron tin plating technology has been demonstrated in some leading vacuum glass manufacturers and is gradually being rolled out to production lines. As equipment develops towards greater intelligence (integrated visual positioning, AI parameter adaptation) and modularity (adapting to different glass sizes and sealing structures), its application potential will be further unleashed.
In the future, this technology will not only solidify its position in high-end building curtain walls and energy-saving doors and windows, but is also expected to promote the large-scale application of vacuum glass in emerging fields such as new energy vehicles (special vehicle windows and battery pack windows), photovoltaic and solar thermal (high-efficiency heat collectors), and display technology (special display packaging), as these fields place higher demands on the lightweight, long lifespan, and reliability of devices in extreme environments.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic soldering iron tin plating technology, this "silent welding torch," is using its unique physical intelligence to solve the sealing problem in vacuum glass manufacturing. It is not merely a process improvement, but a key lever driving the entire industry towards high-quality, high-reliability, and intelligent manufacturing upgrades. When high-frequency mechanical vibrations meet precise temperature control, the edges of vacuum glass are no longer merely seals, but rather a solid link carrying performance, safety, and trust. This silent revolution is redefining the boundaries of "transparency."
Glass, ceramic, stainless steel, and aluminum welding
In extensive research on glass-metal bonding over the years, Japanese engineers have developed a special solder alloy called CERASOLZER (solder wire). This active solder alloy is specifically formulated to work with the ultrasonic soldering method and possesses unique bonding capabilities that can replace commonly used silver soldering, indium brazing, molybdenum-manganese, and resin bonding methods. CERASOLZER forms chemical bonds (glass substrate) in addition to direct metal-to-metal bonding. The alloy consists of the same primary constituents as standard solder alloys (lead/tin), but it also contains small amounts of elements such as zinc, titanium, silicon, aluminum, beryllium, rare earth, etc., which have strong chemical affinities with oxygen.
During the soldering process, these additional elements combine with the surrounding oxygen to form an oxide that chemically bonds with various materials, including glass, ceramics, aluminum, stainless steel, conductive oxides, and many other substrates that were previously considered unsolderable. The resulting oxide bonds strongly with the soldered substrate, forming a robust chemical bond (RO) at the interface.
Therefore, the adhesive strength of CERASOLZER is compromised if oxygen is effectively eliminated by using an inert gas (such as nitrogen) instead of the surrounding air in the bonding equipment. The suitable bonding critical oxygen concentration is found to be around 2%. The melting temperature of the CERASOLZER alloy ranges from 155 to 297°C, and due to the ultrasonic vibration, the soldering method is fluxless. In fact, if our ultrasonic soldering method is used with flux, it would disrupt the oxygen bonds and compromise the entire soldering process, so it should not be used.
Parameter
Frequency 55 Khz Power 100W
Cooling Air cooling Max TEMP 500℃
Protective envelope pomp plastic Power digital generator













