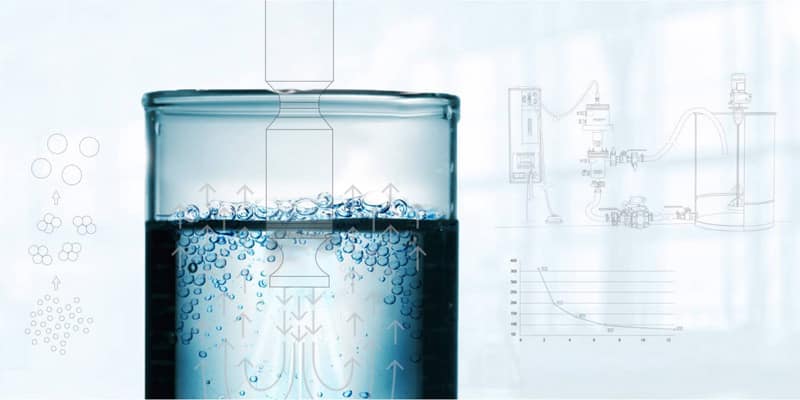
What Is Ultrasonic Plant Herb Extraction?
I.Ultrasonic extraction, also known as ultrasound-assisted extraction, utilizes the cavitation, mechanical, and thermal effects of ultrasound waves (typically 20kHz-100kHz) to rapidly break down plant cell walls, accelerating the dissolution of active ingredients (such as alkaloids, flavonoids, polysaccharides, and essential oils) into the solvent.
II. Core Principles
*Cavitation Effect (Crucial): Ultrasound waves propagating in a liquid generate countless tiny bubbles (cavitation bubbles). These bubbles burst instantaneously, producing localized extreme temperatures (thousands of degrees Celsius), high pressures (thousands of atmospheres), and powerful shock waves, sufficient to break down plant cell walls and cell membranes.
*Mechanical Effect: Ultrasound waves induce high-speed microflow and intense vibrations in the liquid, enhancing diffusion and mass transfer.
*Thermal Effect: A portion of the ultrasound energy is absorbed and converted into heat, moderately raising the system temperature and further promoting the dissolution and diffusion of components.
III. Main Advantages (Compared to Traditional Hot Reflux and Soxhlet Extraction)
High Efficiency: Significantly shortens extraction time, typically requiring only tens of minutes, while traditional methods may require several hours.
High Yield: More thorough cell disruption leads to higher dissolution rates of active ingredients.
Low Temperature/Room Temperature Operation: Can be performed at lower temperatures, ideal for extracting heat-sensitive and easily oxidized active ingredients.
Energy Saving and Environmental Protection: Low energy consumption and relatively low solvent usage.
Easy Operation: Relatively simple equipment, easy to control and scale up.
IV. Basic Process Flow
Raw material pretreatment (washing, drying, pulverizing) → Mixing with solvent (water, ethanol, etc.) → Ultrasonic treatment (setting temperature, power, time) → Filtration/Separation → Concentration → Purification (optional) → Finished Product (Extract)
V. Key Influencing Factors:
Ultrasonic Parameters:
Power/Intensity: Higher power results in stronger cavitation, but excessive power may damage components.
Frequency: Low frequency (20-40kHz) has a strong cavitation effect, suitable for hard materials; high frequency (>100kHz) is gentler, suitable for fine extraction.
Time: Increased time increases yield, but there is an optimal value; excessive time may be ineffective or lead to degradation.
Mode: Pulsed ultrasound reduces thermal effects more effectively than continuous ultrasound.
Raw Material Factors:
Particle Size: Finer particles result in a larger contact area, but excessively fine particles may cause filtration difficulties.
Moisture Content and Structure.
Solvent Factors:
Type of Solvent (polarity matching the target component), concentration (e.g., ethanol concentration), liquid-to-solid ratio (the ratio of solvent to material).
Temperature: Typically controlled between room temperature and 60°C to balance extraction efficiency and protect against heat sensitivity.
VI. Main Application Areas
Pharmaceuticals and Health Products: Extraction of active ingredients from herbs, such as flavonoids, saponins, and alkaloids.
Food Industry: Extraction of natural pigments, flavor substances, antioxidants, and functional components.
Cosmetics: Extraction of plant essential oils, whitening, anti-inflammatory, and moisturizing active ingredients.
Natural Fragrances: Extraction of aromatic components.
VII. Equipment Types
Laboratory Grade: Ultrasonic cleaning machine type, probe type (amplitude bar type, more concentrated energy, higher efficiency).
Industrial Grade: Large ultrasonic extraction tanks, continuous flow ultrasonic extraction systems.
VIII. Limitations and Precautions
Scale-up Effect: Small-scale laboratory parameters cannot be directly applied to industrial production; process optimization is required.
Noise and Corrosion: Industrial equipment may generate noise, and the probe may corrode due to cavitation.
Component Selectivity: More impurities may be extracted simultaneously, potentially placing higher demands on subsequent purification steps.
Unsuitable for Certain Components: Ultrasound may disrupt the structures of some extremely unstable molecules.
Conclusions and Outlook
Ultrasonic herbal extraction is a highly cost-effective and promising green extraction technology. It successfully combines modern physical techniques with traditional herbal resources, demonstrating outstanding performance in terms of "high efficiency, energy saving, and high quality."
Future Development Trends:
Combining with other technologies (such as microwave and enzymatic methods) to create synergistic effects.
Developing more intelligent, modular, and continuous industrial equipment.
In-depth research into the precise influence mechanisms of ultrasound on the structures of complex natural products.
If you are considering specific applications (e.g., extracting a specific component from a particular plant), it is recommended to start with small-scale laboratory tests, systematically optimizing key parameters such as power, time, temperature, solvent, and solid-liquid ratio to find the optimal process conditions.