Ultrasonic Sterilization and inactivation Technology
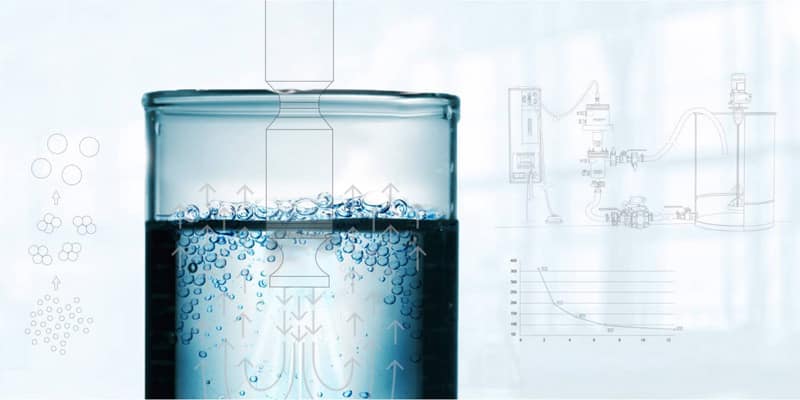
Ultrasonic sterilization, also known as ultrasound-assisted sterilization, is a technology that uses high-frequency sound waves (typically > 20 kHz) to destroy or inactivate microorganisms (such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi). Ultrasonic sterilization utilizes the cavitation effect of ultrasound to generate extreme temperatures and pressures in liquids, thereby destroying microbial cell walls and achieving sterilization. Ultrasonic sterilization can be used alone or in conjunction with other sterilization methods to enhance effectiveness, reduce requirements, or shorten the duration of the process.
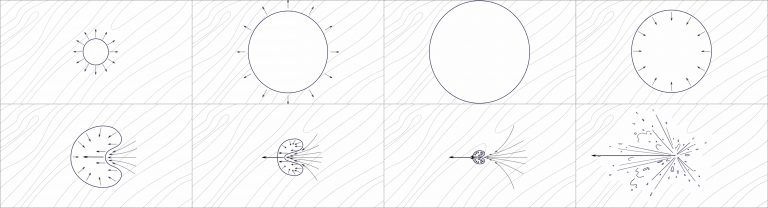
Cavitation Process:
Generation and Growth: When high-intensity ultrasound propagates through a liquid medium, it creates alternating zones of compression and rarefaction. In the rarefaction zones, the liquid is stretched, creating tiny bubbles or cavities within them.
Violent Collapse: These bubbles are rapidly compressed by the subsequent compression wave and violently collapse within a very short time (on the order of microseconds), generating localized extreme temperatures (approximately 5000K), pressures (approximately 1000 atmospheres), and intense shock waves.
Destructive Effect:
Mechanical Shear: The shock wave and microfluidics exert tremendous shear forces on nearby microbial cell walls/membranes, rupturing them and leaking their contents, leading to cell death. Chemical Free Radicals: High temperature and high pressure cause water molecules to break down, producing large quantities of hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and hydrogen radicals (·H). These highly reactive free radicals can attack microbial cell membranes, enzymes, and DNA, inactivating them.
Simply put, ultrasound acts like a "microscopic explosion" in liquids, destroying microorganisms through both physical fragmentation and chemical oxidation.
Main Applications:
Ultrasonic sterilization, due to its advantages such as high temperature resistance, no chemical residue, and ability to treat complex surfaces, has shown great potential in a variety of fields.
1. Food Industry
This is one of the most widely used areas for ultrasonic sterilization.
Liquid Food: Used for sterilizing juice, milk, soy sauce, beverages, etc. Compared to traditional pasteurization, it better preserves the flavor, color, and nutritional content of foods.
Surface Sterilization: Used to clean and sterilize pathogens (such as E. coli and Salmonella) attached to the surfaces of fruits, vegetables, meat, and aquatic products.
Packaging Materials: Sterilizes the interior of food packaging containers such as cans and Tetra Pak cartons. Synergistic Sterilization: When combined with mild heating (thermosonication), moderate pressure (manosonication), or a small amount of chemical disinfectant, the temperature, pressure, or chemical dosage required for sterilization can be significantly reduced, achieving a "green" process.
2. Medical and Biotechnology
Medical Device Cleaning and Sterilization: Ultrasonic cleaning machines are standard equipment in hospitals and dental clinics. They effectively remove biofilm, blood, and pathogens from crevices and corners of instruments, preparing them for subsequent high-pressure steam sterilization.
Pharmaceutical and Vaccine Production: They are used to process heat-sensitive pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and culture media, ensuring their sterility without destroying the active ingredients.
Wound Debridement: Low-intensity ultrasound can be used to remove necrotic tissue and bacteria from wounds, promoting healing.
3. Water Treatment: Used to treat drinking water, swimming pool water, and industrial wastewater. They effectively kill algae, bacteria, and viruses in water and degrade organic pollutants. They are even more effective when used in combination with ultraviolet light or ozone.
4. Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
Ensures sterile production of heat-labile liquid medicines, eye drops, skincare products, and cosmetics.
Advantages:
Non-thermal processing: Particularly suitable for processing heat-sensitive substances, preserving the product's original quality to the greatest extent possible.
No chemical residue: Avoids residual issues associated with chemical disinfectants, making it safer and more environmentally friendly.
High penetration: Capable of treating microorganisms within liquids and on irregular surfaces, eliminating dead spots.
Strong synergy: Combined with other technologies, it can significantly improve efficiency, reduce overall costs, and reduce product damage.